Do you want to know what is a domain name and how does it work?
Domain names are an essential part of more than 1.5 billion websites on the internet. However, tons of people still find them hard to understand.
Most times, beginners mix up domains with web hosting or website, but they’re not the same. Rather, they’re the different things closely linked to each other.
In this article, we’ll explain what a domain name is, how it works, what is it used for, and everything you need to know about domain names. Also, we’ll share how domains are related to hosting and websites.
Let’s get started!
What is a Domain Name? – Definition
In the simplest terms, a domain name is the name and address of a website.
Just like each one of us has a name and an address, every website on the internet has a name and address. The name gives the site a unique identity on the internet and the address shows where the website can be accessed. However, it’s the same – a domain name.
For example; google.com is a domain name. It is the name of the search engine website. It’s also the address of the website because this is what internet users type in their web browser’s address bar to open Google.
Similarly, www.sitesaga.com is the domain name of our website.
It’s both the name and address of our website. This is our website’s name because it identifies our website among millions of websites on the web. And, it’s our site’s address because our users including you need to type this in your browser’s address bar to access our website.
The basic idea behind the domain name is to provide the address of your website to global users.
The Internet is a network of interconnected computers globally. These computers can communicate and transmit information from one another.
In the process, each computer is assigned a unique Internet Protocol (IP) address. An IP address is a numerical label that helps to identify one computer from others on the web. An IP address looks like this:
66.220.144.0
As you can see, the IP addresses are complex and difficult to memorize.
To solve this problem, domain names were invented. Rather than remembering the numeral keys for each website, you need to remember just a simple name.
Like, if you’re a regular Facebook user, you can just put facebook.com in the address bar of your browser and you can easily get in there.
Some examples of domain names are:
- sitesaga.com
- google.com
- facebook.com
How Does a Domain Name work?
When an internet user enters a domain in the search bar of the browser, the browser then connects to the Domain Name System (DNS).
The Domain Name System is a large network of servers that contain information about the domains and IP addresses. It’s like an address book where domain names are stored with their associated IP addresses.
Upon the browser’s request, DNS servers look for the IP address linked to the requested domain. When the IP address is found, the DNS servers then point the browser to it.
The IP address is the actual location where the website is stored, called the web hosting server.
After that, the browser connects to the hosting server and sends a request to show the website. Next, the web host fetches the requested page to the browser, and we can see it on the computer screen.
Difference Between Domain and Web Hosting
The domain and web hosting are 2 essential things required to make a website available on the web. They work together to make a website appear online on the internet. However, beginners often confuse them with one another.
As stated above, the domain name is the address of your website on the internet. Web hosting is the actual location where your website is located.
In other words, web hosting is the house where your site lives and the domain is the address of that house. Web hosting is the actual computer where your website files are stored.
For more details, see our definitive article on what is web hosting.
A domain works just like your home address does. With your home address, people can find out where you live and come to visit your house. Similarly, with your domain, internet users can easily find and visit your website.
So, when a user enters your domain name into the browser’s address bar, the browser connects to the web hosting where your website files are stored and shows the requested web page.
Parts of a Domain Name
Now that you know what a domain is, let’s see how it’s formed.
A domain name comprises 2 parts: Second level domain and Top-level domain.
1. Second Level Domain
This is the major part of a domain. While you register a domain for yourself, the name you choose depending upon the availability is the Second Level Domain.
For example, ‘sitesaga’ is the second-level domain of the domain name ‘www.sitesaga.com’.

In other words, it is the word between the two dots in a URL.
For example, the URL of our website is ‘https://www.sitesaga.com/’. In this URL, the word after ‘https://www.’ and before ‘.com’ is the second-level domain.
2. Top-Level Domain
The domain extension or top-level domain is the end part of a domain name. In www.sitesaga.com, ‘.com’ is the top-level domain (TLD).

There are variations available for the top-level domains such as .org, .net, .info, .gov etc. according to the purpose of use. For example, .com is used for commercial websites, .org for organizations, .gov for government, etc.
Among all the TLDs, ‘.com’ is the most popular one.
Is a Domain Name Same as a URL ?
Another common confusion among beginners is between a URL and a domain. It’s quite obvious because they look almost the same.
Uniform Resource Locator (URL) is the complete web address that leads to a specific page on a website. A URL at the minimum consists of the domain name and scheme (https:// or http://).
For example, the URL of our website is: https://www.sitesaga.com/
Whereas our site’s domain name is: www.sitesaga.com.
The above URL leads to our website’s home page. Similarly, other pages on our website can be accessed by their specific URLs.
The URLs of other pages can have various other components like subdomain, subdirectory, file path, etc.
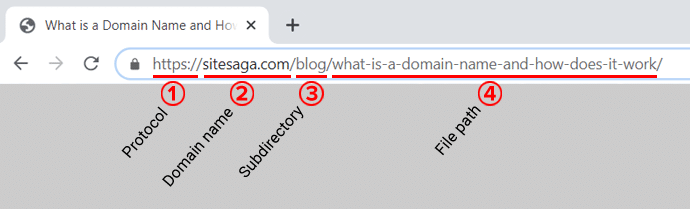
For example, let’s see the URL of this article: https://www.sitesaga.com/blog/what-is-a-domain-name-and-how-does-it-work/
This URL consists of 4 components;
- scheme (https://),
- domain name (www.sitesaga.com),
- subdirectory (/blog/), and
- file path (/what-is-a-domain-name-and-how-does-it-work/).
In the nutshell, the domain is a website’s name. This also works as the site’s homepage address.
Whereas, a URL is the full web address of a web page. It includes the domain name, scheme, and other things.
How to Choose a Perfect Domain name?
As stated above, the domain is your website’s name i.e. your identity on the web. It may be a personal portfolio website, a business website, or any type of site, your domain plays a vital role in making your brand.
However, choosing a good domain isn’t so easy. Since there’re millions of domain names already registered, you can barely find a name of your choice.
Here are some tips to help you choose a cool domain for your website.
1. Try to Stick With .com Domain Extension
Most of the popular websites end with the .com extension which prepares our mindset to believe ‘.com’ as an obvious extension of every domain. Statistics show that approximately 47% of the website today use the ‘.com’ extension.

Rare but sometimes even the search engines prefer ‘.com’ domains over other domains. This is not always true, but it has been found that ‘.com’ as a universal domain does well instead of regional domains such as ‘.us’, ‘.in’, ‘.uk’, etc.
So, it’s wise to stick with a ‘.com’ domain.
2. Choose a Short, Simple, and Spellable Name
It’s better to choose a short, simple, and spellable domain name over a long or complex name. Having a short and simple domain has several various benefits.
To mention a few, first, it’s easy to remember, so users can memorize your brand name without putting in any effort. This helps with your website’s branding.
Second, they cannot go wrong while searching your website in Google or while typing in your domain in the web browser. Many sites lose visitors because of the complex name but you’ll get 100% of your audience.
3. Use Keywords to Get Domain Idea
Instead of using random words, using your business name for which you want to rank is beneficial. It improves your website’s Search Engine Optimization (SEO) and helps to rank better in search results.
4. Avoid Hyphens and Numbers in your Domain
You should seek a unique name for your website but hyphens and numbers in your domain unknowingly harm your site.
When you use hyphens and numbers, your website name becomes somewhat difficult to remember. Your audience may not always remember the hyphens and numbers. As a result, they may land on somebody’s website or end up with no result.
5. Use a Domain Name Generator Tool
There are numerous domain name generator tools online which can help you find a perfect name for your website.
With a domain name generator tool, you can easily get website name ideas and also see if a name is available or already taken. Simply enter a keyword in the domain name generator tool and then it will come up with many relevant domain ideas.
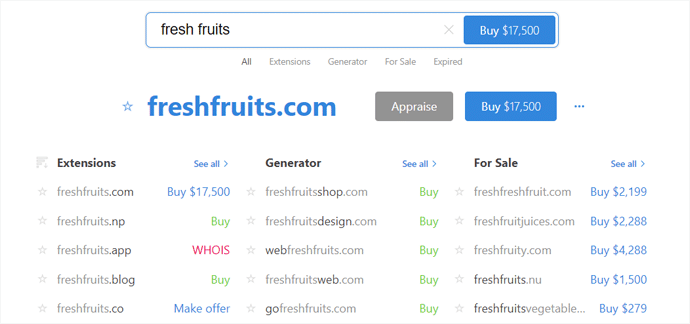
If you want to know more, see our detailed article on domain name generators.
Where to Buy a Domain Name?
The domain is one of the first things you should buy to start a website. It provides your website with an identity on the web and helps internet users to find your website easily.
You can buy domain names from companies called ‘domain registrars‘. They’re the businesses accredited by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) to sell domain names to the public.
But this statement ‘buying a domain name’ is a bit tricky because you cannot buy a domain outright or permanently. But you can register a domain for a certain period. This is like renting an apartment from an apartment complex.
But it doesn’t mean that you have to forget your domain once the lease time ends. You can renew the registration continually and keep using it as long as you want. You can register most domains for 1 year, however, some domain extensions may be available for 2 years to 10 years.
Here’re some of the popular domain registrars where you can register a domain name:
On average, a new domain costs between $10 to $20 a year. However, it varies from free to million bucks depending upon the type of domain you want to register.
Some web hosting companies and website builders offer free domain names when you purchase a hosting plan or create a website on their platform. You can use a free domain if you’re on a budget.
For example, if you buy web hosting from Bluehost, then you’ll get a domain free of cost.
Their basic hosting plan costs $2.95 per month, so you can start a website as low as this amount.
If you need a step-by-step guide, then please see our complete guide on how to make a website.
Wrapping Up
We hope this article helped you to understand what a domain name is, how it works, why you need one, and how to get one.
If you’re planning to start a new website, then take some time for domain research. It’s important because your domain name plays a vital role in the marketing, branding, and overall success of your site.
If you liked this article, then you may also want to see our article on the best blogging platforms.
If you have any feedback or want to share anything about domains, then please comment below. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Facebook and Twitter.